Materiality
DNP identifies materiality to realize the “better future” it envisions.
The roadmap to the "better future" that DNP aims for and the path to its realization
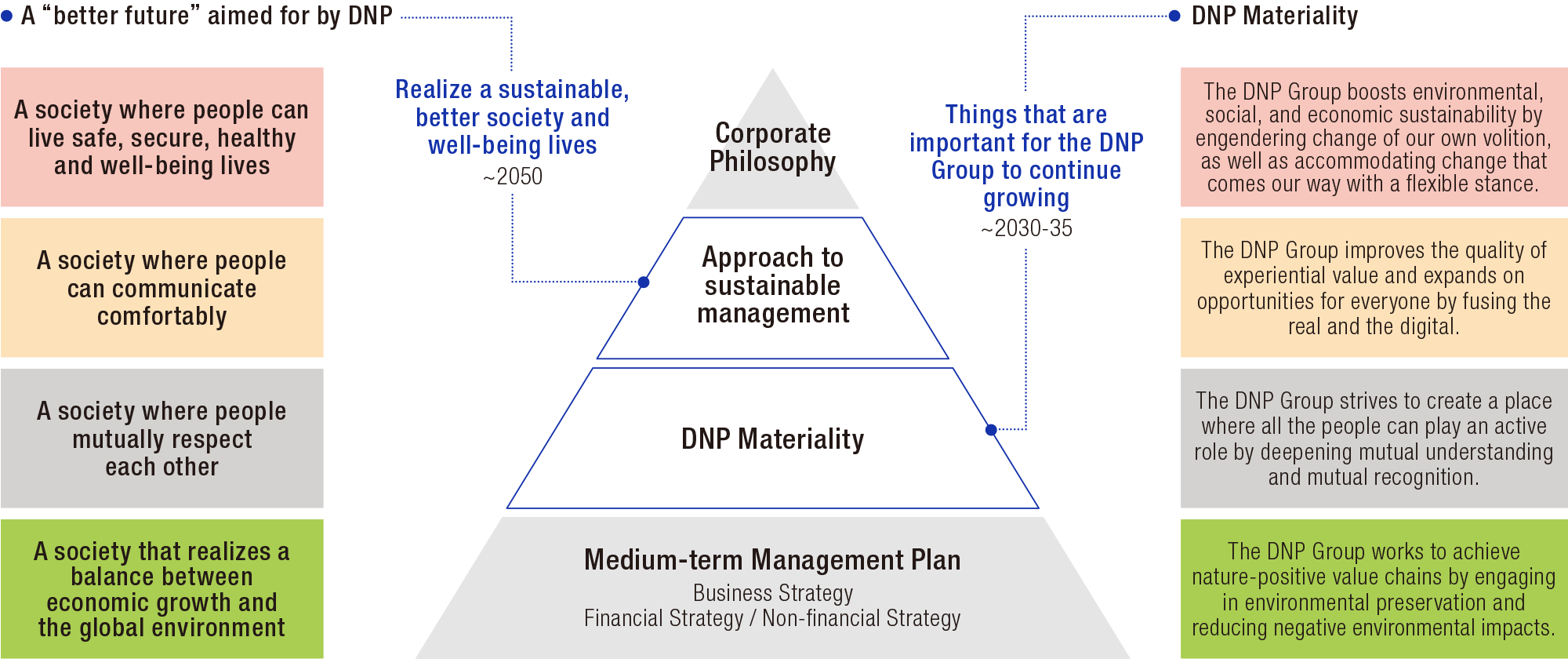
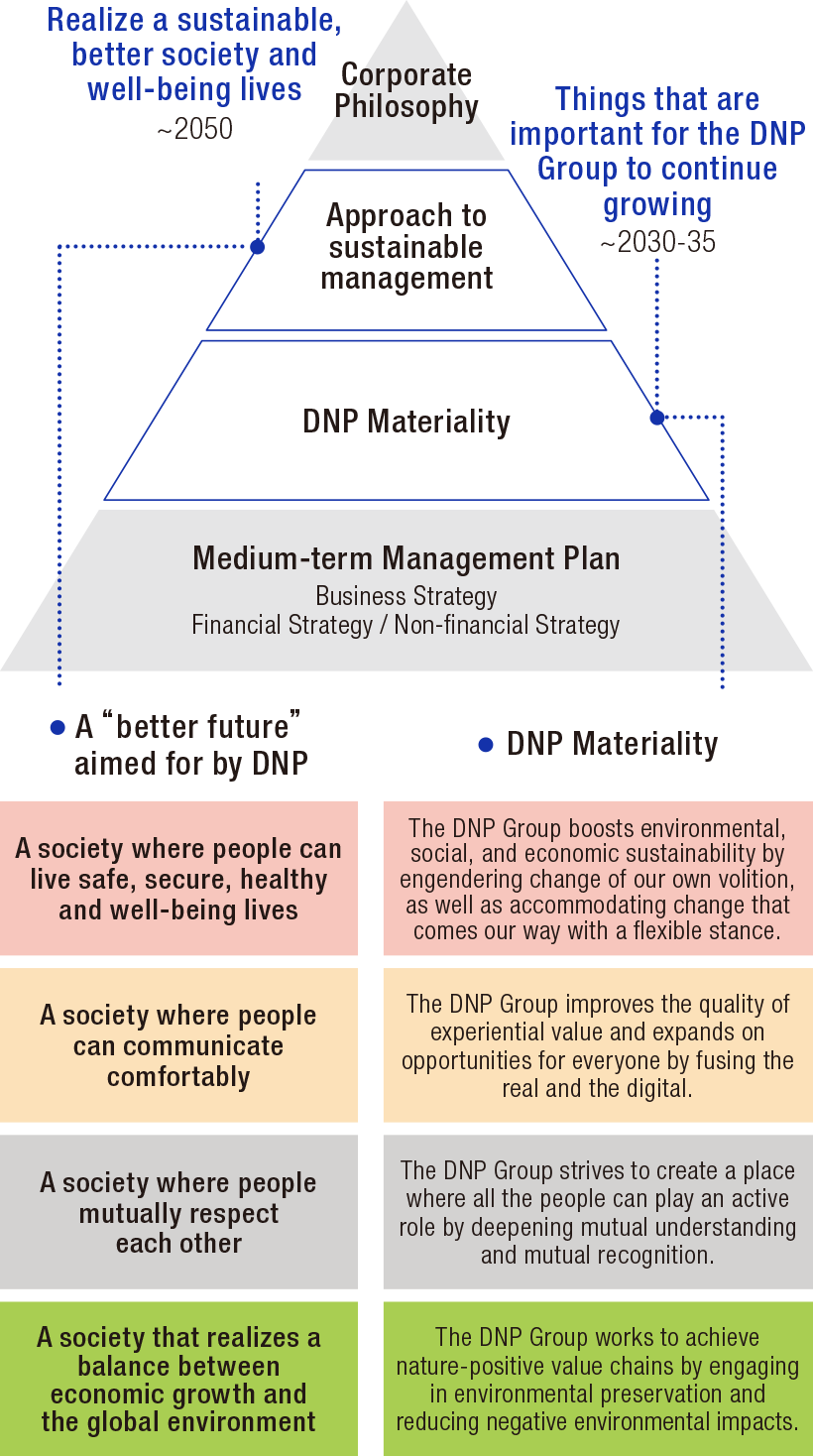
Based on the Corporate Philosophy, the DNP Group aims to realize “a sustainable, better society and well-being lives" as a sustainable management concept and is taking the initiative in conducting business activities to create a “better future.”
To realize the four interrelated societies that it aims for as a “better future,” in March 2024 DNP identified materiality as important for it to continuously grow together with society by specifying what DNP should do and what value it will create with an eye toward 2030-35.
A “better future” aimed for by DNP
DNP Groupʼs Philosophy and Materiality
Process for identifying materiality
We comprehensively grasp social issues and mega-trends related to the environment, society, and economy, and identify and evaluate medium- to long-term risks (variables) in DNP's business activities, as well as identify and prioritize social issues that are highly important for DNP and society stakeholders.
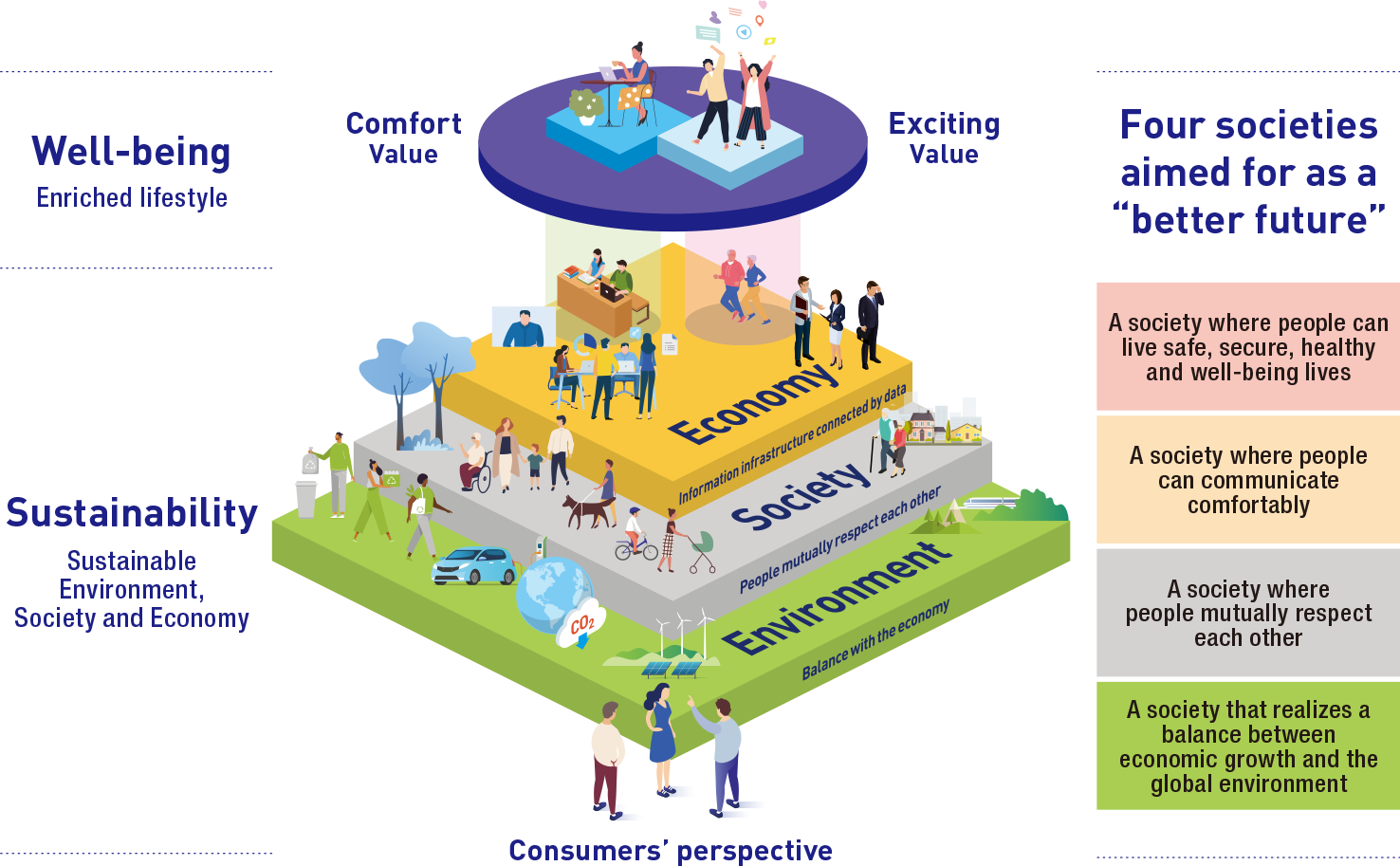
Initiatives to realize the “four societies” envisioned by DNP
A society where people can live safe, secure, healthy and well-being lives
The DNP Group boosts environmental, social, and economic sustainability by engendering change of our own volition, as well as accommodating change that comes our way with a flexible stance.
Main initiatives
A society where people can communicate comfortably
The DNP Group improves the quality of experiential value and expands on opportunities for everyone by fusing the real and the digital.
Main initiatives
A society where people mutually respect each other
The DNP Group strives to create a place where all the people can play an active role by deepening mutual understanding and mutual recognition.
Main initiatives
A society that realizes a balance between economic growth and the global environment
The DNP Group works to achieve nature-positive value chains by engaging in environmental preservation and reducing negative environmental impacts.
Main initiatives
The PDF version of the integrated report introduces DNP's initiatives towards achieving a "better future," including the main strategies of each business division.
To create a "better future" by taking the initiative oneself
Thorough risk management to support sustainable growth
We are thoroughly implementing risk management that supports sustainable growth and responds to sustainability-related risks and opportunities.